Phrase Match
短语匹配允许您搜索包含查询词为精确短语的文档。默认情况下,这些词必须按相同顺序且彼此直接相邻出现。例如,查询 "robotics machine learning" 会匹配类似 "…typical robotics machine learning models…" 这样的文本,其中 "robotics"、"machine" 和 "learning" 按顺序出现,中间没有其他词。
然而,在现实场景中,严格的短语匹配可能过于死板。你可能希望匹配类似*"…machine learning models widely adopted in robotics…"*这样的文本。这里,相同的关键词存在,但并非相邻或按原始顺序排列。为处理这种情况,短语匹配支持 slop 参数,该参数引入了灵活性。slop 值定义了短语中各词项之间允许的位置偏移数量。例如,当slop 值为 1 时,对 "machine learning" 的查询可以匹配类似 "...machine deep learning..." 这样的文本,其中一个词("deep")分隔了原始词项。
概述
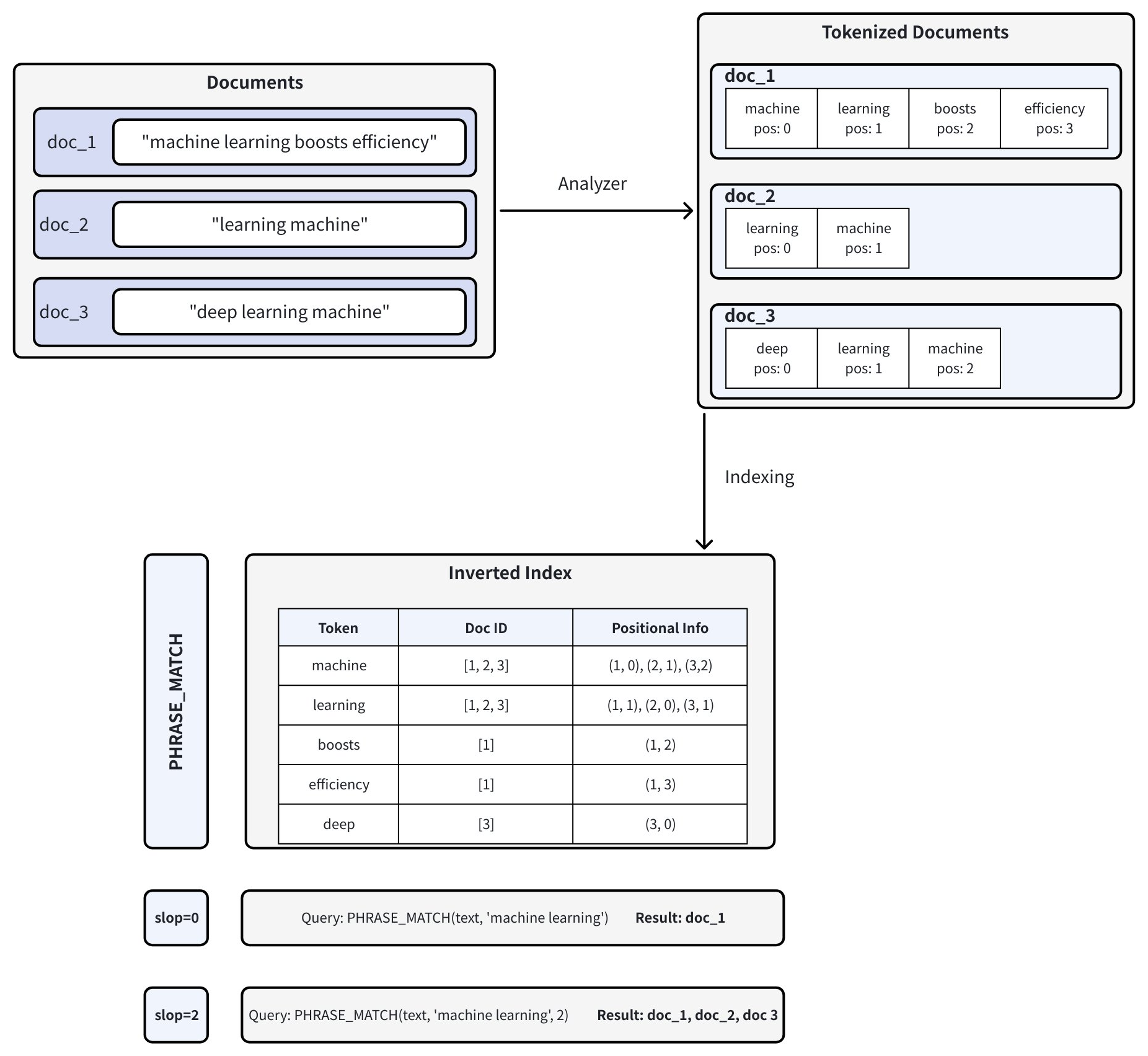
由 Tantivy 搜索引擎库提供支持,短语匹配通过分析文档中单词的位置信息来工作。下图说明了该过程:
-
文档分词:当您将文档插入 Zilliz Cloud 时,文本会被 Analyzer 拆分为词元(单个单词或术语),并记录每个词元的位置信息。例如,doc_1 被分词为 ["machine" (pos=0), "learning" (pos=1), "boosts" (pos=2), "efficiency" (pos=3)]。有关 Analyzer 的更多信息,请参阅Analyzer 概述。
-
创建倒排索引:Zilliz Cloud 构建倒排索引,将每个词项映射到其出现的文档以及该词项在这些文档中的位置。
-
短语匹配:执行短语查询时,Zilliz Cloud 会在倒排索引中查找每个词元,并检查它们的位置,以确定它们是否按正确的顺序和邻近度出现。
slop参数控制匹配词元之间允许的最大位置数:-
slop = 0 表示这些词项必须按确切顺序且紧邻出现 (即,中间没有额外的词)。
- 在示例中,只有doc_1("machine"在pos=0,"learning"在pos=1)完全匹配。
-
slop = 2允许匹配的词元之间最多有两个位置的灵活性或重排。
-
这允许反转顺序(“学习机”)或标记之间存在小间隙。
-
因此,doc_1、doc_2("learning"在pos=0,"machine"在pos=1)和doc_3("learning"在pos=1,"machine"在pos=2)都匹配。
-
-
开启词组匹配
短语匹配适用于 VARCHAR 字段类型,即 Zilliz Cloud 中的字符串数据类型。
要启用短语匹配,请通过将 enable_analyzer 和 enable_match 参数都设置为 True 来配置 Collection Schema。此配置会对文本进行分词,并基于位置信息构建倒排索引,从而实现高效的短语匹配查询。
定义字段类型
若要为特定的 VARCHAR 字段启用短语匹配,请在定义字段 Schema 时将 enable_analyzer 和 enable_match 参数都设置为 True。
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- Go
- cURL
from pymilvus import MilvusClient, DataType
# Set up a MilvusClient
CLUSTER_ENDPOINT = "YOUR_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT"
TOKEN = "YOUR_CLUSTER_TOKEN"
client = MilvusClient(
uri=CLUSTER_ENDPOINT,
token=TOKEN
)
# Create a schema for a new collection
schema = client.create_schema(enable_dynamic_field=False)
# Add a primary key field
schema.add_field(
field_name="id",
datatype=DataType.INT64,
is_primary=True,
auto_id=True
)
# Add a VARCHAR field configured for phrase matching
schema.add_field(
field_name="text", # Name of the field
# highlight-next-line
datatype=DataType.VARCHAR, # Field data type set as VARCHAR (string)
max_length=1000, # Maximum string length
# highlight-start
enable_analyzer=True, # Required. Enables text analysis
enable_match=True, # Required. Enables inverted indexing for phrase matching
# highlight-end
# Optional: Use a custom analyzer for better phrase matching in specific languages.
# analyzer_params = {"type": "english"} # Example: English analyzer; uncomment to apply custom analyzer
)
# Add a vector field for embeddings
schema.add_field(
field_name="embeddings",
datatype=DataType.FLOAT_VECTOR,
dim=5
)
import io.milvus.v2.common.DataType;
import io.milvus.v2.service.collection.request.AddFieldReq;
import io.milvus.v2.service.collection.request.CreateCollectionReq;
MilvusClientV2 client = new MilvusClientV2(ConnectConfig.builder()
.uri("YOUR_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT")
.token("YOUR_CLUSTER_TOKEN")
.build());
CreateCollectionReq.CollectionSchema schema = CreateCollectionReq.CollectionSchema.builder()
.build();
schema.addField(AddFieldReq.builder()
.fieldName("id")
.dataType(DataType.Int64)
.isPrimaryKey(true)
.autoID(true)
.build());
schema.addField(AddFieldReq.builder()
.fieldName("text")
.dataType(DataType.VarChar)
.maxLength(1000)
.enableAnalyzer(true)
.enableMatch(true)
// Optional: Use a custom analyzer for better phrase matching in specific languages.
// .analyzerParams(Map.of("type", "english")) // Example: English analyzer; uncomment to apply custom analyzer
.build());
schema.addField(AddFieldReq.builder()
.fieldName("embeddings")
.dataType(DataType.FloatVector)
.dimension(5)
.build());
// Set up a MilvusClient
const address = "YOUR_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT"
const token = "YOUR_CLUSTER_TOKEN"
const client = new MilvusClient({address, token})
const schema = {
collection_name: 'tech_articles',
fields: [
{
name: "id",
description: "primary id",
data_type: DataType.Int64,
is_primary_key: true,
autoID: true,
},
{
name: "text",
description: "text field for phrase matching",
data_type: DataType.VarChar,
max_length: 1000,
enable_analyzer: true, // Enables text analysis
enable_match: true, // Enables inverted indexing for
},
{
name: "embeddings",
description: "vector field",
data_type: DataType.FloatVector,
dim: 5,
},
],
};
import (
"github.com/milvus-io/milvus/client/v2/entity"
)
milvusAddr := "YOUR_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT"
APIKey := "YOUR_API_KEY"
client, err := milvusclient.New(ctx, &milvusclient.ClientConfig{
Address: milvusAddr,
APIKey: APIKey
})
schema := entity.NewSchema().WithName(collectionName).
WithField(entity.NewField().WithName("id").WithDataType(entity.FieldTypeInt64).WithIsPrimaryKey(true)).
WithField(entity.NewField().WithName("text").WithDataType(entity.FieldTypeVarChar).WithMaxLength(1000).WithEnableMatch(true).WithEnableAnalyzer(true)).
WithField(entity.NewField().WithName("embeddings").WithDataType(entity.FieldTypeFloatVector).WithDim(5))
export idField='{
"fieldName": "id",
"dataType": "Int64",
"isPrimary": true,
"autoID": true
}'
export textField='{
"fieldName": "text",
"dataType": "VarChar",
"elementTypeParams": {
"max_length": 1000,
"enable_analyzer": true,
"enable_match": true
}
}'
export vectorField='{
"fieldName": "embeddings",
"dataType": "FloatVector",
"elementTypeParams": {
"dim": 5
}
}'
export schema="{
\"autoID\": false,
\"enableDynamicField\": true,
\"fields\": [
$idField,
$textField,
$vectorField
]
}"
默认情况下,Zilliz Cloud 使用 standard analyzer,该分析器会根据空格和标点对文本进行分词,并将文本转换为小写。
如果你的文本数据使用特定语言或格式,可以通过 analyzer_params 参数配置自定义分析器(例如 { "type": "english" } 或 { "type": "jieba" })。
详细信息请参阅 Analyzer 概述。
创建 Collection
字段定义完成后,参考如下代码创建 Collection:
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- Go
- cURL
# Create the collection
COLLECTION_NAME = "tech_articles" # Name your collection
if client.has_collection(COLLECTION_NAME):
client.drop_collection(COLLECTION_NAME)
client.create_collection(
collection_name=COLLECTION_NAME,
schema=schema
)
String COLLECTION_NAME = "tech_articles"; // Name your collection
if (client.hasCollection(
HasCollectionReq.builder()
.collectionName(COLLECTION_NAME)
.build()
)) {
client.dropCollection(
DropCollectionReq.builder()
.collectionName(COLLECTION_NAME)
.build()
);
}
client.createCollection(
CreateCollectionReq.builder()
.collectionName(COLLECTION_NAME)
.collectionSchema(schema)
.build()
);
// Create or recreate the collection if it already exists
const COLLECTION_NAME = "tech_articles"; // Name your collection
const hasCollection = await client.hasCollection({ collection_name: COLLECTION_NAME });
if (hasCollection.value) {
await client.dropCollection({ collection_name: COLLECTION_NAME });
}
await client.createCollection(schema);
// go
# restful
# check collection exist
export MILVUS_HOST="localhost:19530"
export COLLECTION_NAME="tech_articles"
curl -X POST "YOUR_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT/v2/vectordb/collections/has" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d "{
\"collectionName\": \"$COLLECTION_NAME\"
}"
# drop existing collection
curl -X POST "http://${MILVUS_HOST}/v2/vectordb/collections/drop" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d "{
\"collectionName\": \"${COLLECTION_NAME}\"
}"
# create new collection
curl --request POST \
--url "${CLUSTER_ENDPOINT}/v2/vectordb/collections/create" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--data "{
\"collectionName\": \"$COLLECTION_NAME\",
\"schema\": $schema
}"
创建 Collection 后,在使用 Phrase Match 之前,请确保完成以下必要步骤:
-
向 Collection 中插入 Entity;
-
为每个向量字段创建索引;
-
将 Collection 加载到内存中。
Show example code
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- Go
- cURL
# Insert sample data with text containing "machine learning" phrases
sample_data = [
{
"text": "Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence that focuses on algorithms.",
"embeddings": [0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5]
},
{
"text": "Deep learning machine algorithms require large datasets for training.",
"embeddings": [0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6]
},
{
"text": "The machine learning model showed excellent performance on the test set.",
"embeddings": [0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7]
},
{
"text": "Natural language processing and machine learning go hand in hand.",
"embeddings": [0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8]
},
{
"text": "This article discusses various learning machine techniques and applications.",
"embeddings": [0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9]
}
]
# Insert the data
client.insert(
collection_name=COLLECTION_NAME,
data=sample_data
)
# Index the vector field and load the collection
index_params = client.prepare_index_params()
index_params.add_index(
field_name="embeddings",
index_type="AUTOINDEX",
index_name="embeddings_index",
metric_type="COSINE"
)
client.create_index(collection_name=COLLECTION_NAME, index_params=index_params)
client.load_collection(collection_name=COLLECTION_NAME)
// Insert sample data with text containing "machine learning" phrases
List<JsonObject> sampleData = Arrays.asList(
createSample("Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence that focuses on algorithms.", new float[]{0.1f, 0.2f, 0.3f, 0.4f, 0.5f}),
createSample("Deep learning machine algorithms require large datasets for training.", new float[]{0.2f, 0.3f, 0.4f, 0.5f, 0.6f}),
createSample("The machine learning model showed excellent performance on the test set.", new float[]{0.3f, 0.4f, 0.5f, 0.6f, 0.7f}),
createSample("Natural language processing and machine learning go hand in hand.", new float[]{0.4f, 0.5f, 0.6f, 0.7f, 0.8f}),
createSample("This article discusses various learning machine techniques and applications.", new float[]{0.5f, 0.6f, 0.7f, 0.8f, 0.9f})
);
client.insert(InsertReq.builder()
.collectionName(COLLECTION_NAME)
.data(sampleData)
.build());
// Index the vector field and load the collection
IndexParam indexParam = IndexParam.builder()
.fieldName("embeddings")
.indexType(IndexParam.IndexType.AUTOINDEX)
.indexName("embeddings_index")
.metricType(IndexParam.MetricType.COSINE)
.build();
client.createIndex(CreateIndexReq.builder()
.collectionName(COLLECTION_NAME)
.indexParams(Collections.singletonList(indexParam))
.build());
client.loadCollection(LoadCollectionReq.builder()
.collectionName(COLLECTION_NAME)
.build());
// Format and insert sample data for "machine learning" phrase matching
const sampleData = [
{
text: "Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence that focuses on algorithms.",
embeddings: [0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5],
},
{
text: "Deep learning machine algorithms require large datasets for training.",
embeddings: [0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6],
},
{
text: "The machine learning model showed excellent performance on the test set.",
embeddings: [0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7],
},
{
text: "Natural language processing and machine learning go hand in hand.",
embeddings: [0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8],
},
{
text: "This article discusses various learning machine techniques and applications.",
embeddings: [0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9],
},
];
// Insert the data into the collection
await client.insert({
collection_name: COLLECTION_NAME,
data: sampleData,
});
// Create an index on the vector field and load the collection
await client.createIndex({
collection_name: COLLECTION_NAME,
field_name: "embeddings",
index_type: "AUTOINDEX",
index_name: "embeddings_index",
metric_type: "COSINE",
});
await client.loadCollection({
collection_name: COLLECTION_NAME,
});
// go
# restful
# Insert the data into the collection
curl -X POST "YOUR_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT/v2/vectordb/entities/insert" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <token>" \
-d '{
"collectionName": "tech_articles",
"data": [
{
"text": "Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence that focuses on algorithms.",
"embeddings": [0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5]
},
{
"text": "Deep learning machine algorithms require large datasets for training.",
"embeddings": [0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6]
},
{
"text": "The machine learning model showed excellent performance on the test set.",
"embeddings": [0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7]
},
{
"text": "Natural language processing and machine learning go hand in hand.",
"embeddings": [0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8]
},
{
"text": "This article discusses various learning machine techniques and applications.",
"embeddings": [0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9]
}
]
}'
# Create an index on the vector field and load the collection
curl -X POST "YOUR_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT/v2/vectordb/indexes/create" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <token>" \
-d '{
"collectionName": "tech_articles",
"indexParams": [
{
"fieldName": "embeddings",
"indexName": "embeddings_index",
"metricType": "COSINE",
"indexType": "AUTOINDEX"
}
]
}'
curl -X POST "YOUR_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT/v2/vectordb/collections/load" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <token>" \
-d '{
"collectionName": "tech_articles"
}'
使用词组匹配
在 Collection Schema 中为 VARCHAR 字段启用匹配后,您可以使用 PHRASE_MATCH 表达式执行短语匹配。
PHRASE_MATCH 表达式不区分大小写。您可以使用 PHRASE_MATCH 或 phrase_match。
PHRASE_MATCH 表达式语法
使用 PHRASE_MATCH 表达式在搜索时指定字段、短语和可选的灵活性(slop)。语法如下:
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- Go
- cURL
PHRASE_MATCH(field_name, phrase, slop)
String filter = "PHRASE_MATCH(text, 'machine learning')";
PHRASE_MATCH(field_name, phrase, slop)
// go
# restful
export filter = "PHRASE_MATCH(field_name, phrase, slop)"
-
field_name:您执行短语匹配的VARCHAR字段的名称。 -
phrase:要搜索的确切短语。 -
slop(可选):一个整数,指定匹配标记中允许的最大位置数。-
0(默认):仅匹配精确短语。示例:匹配目标为 "machine learning" 的过滤表达式将精确匹配 "machine learning",但不匹配 "machine boosts learning" 或 "learning machine"。 -
1:允许细微变化,例如多一个词或位置稍有偏移。示例:匹配目标为 "machine learning" 的过滤表达式将匹配 "machine boosts learning"("machine" 和 "learning" 之间有一个词),但不匹配 "learning machine"(词序颠倒)。 -
2:允许更多灵活性,包括颠倒词序或中间最多两个词。示例:匹配目标为 "machine learning" 的过滤表达式将匹配 "learning machine"(词序颠倒)或 "machine quickly boosts learning"("machine" 和 "learning" 之间有两个词)。
-
短语匹配查询
使用 query() 方法时,PHRASE_MATCH 用作标量过滤条件。此时,查询仅返回包含指定短语(允许有一定的间隔)的文档。
示例:slop = 0(完全匹配)
此示例返回包含确切短语 "machine learning" 且中间没有任何额外内容的文档。
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- Go
- cURL
# Match documents containing exactly "machine learning"
filter = "PHRASE_MATCH(text, 'machine learning')"
result = client.query(
collection_name=COLLECTION_NAME,
# highlight-next-line
filter=filter,
output_fields=["id", "text"]
)
print("Query result: ", result)
# Expected output:
# Query result: data: ["{'id': 461366973343948097, 'text': 'Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence that focuses on algorithms.'}", "{'id': 461366973343948099, 'text': 'The machine learning model showed excellent performance on the test set.'}", "{'id': 461366973343948100, 'text': 'Natural language processing and machine learning go hand in hand.'}"]
import io.milvus.v2.service.vector.request.QueryReq;
import io.milvus.v2.service.vector.response.QueryResp;
String filter = "PHRASE_MATCH(text, 'machine learning')";
QueryResp result = client.query(QueryReq.builder()
.collectionName(COLLECTION_NAME)
.filter(filter)
.outputFields(Arrays.asList("id", "text"))
.build());
const filter = "PHRASE_MATCH(text, 'machine learning')";
const result = await client.query({
collection_name: COLLECTION_NAME,
filter: filter,
output_fields: ["id", "text"]
});
// go
# restful
curl -X POST "YOUR_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT/v2/vectordb/entities/query" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <token>" \
-d '{
"collectionName": "tech_articles",
"filter": "PHRASE_MATCH(text, '\''machine learning'\'')",
"outputFields": ["id", "text"],
"limit": 100
}'
按短语匹配搜索
在搜索操作中,PHRASE_MATCH 用于在应用向量相似度排序之前对文档进行预过滤。这种两步法首先通过文本匹配缩小候选集,然后根据向量嵌入对这些候选进行重新排序。
示例:slop = 1
在这里,我们允许有1的容差。该过滤器应用于包含短语 "learning machine" 的文档,具有一定的灵活性。
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- Go
- cURL
# Example: Filter documents containing "learning machine" with slop=1
filter_slop1 = "PHRASE_MATCH(text, 'learning machine', 1)"
result_slop1 = client.search(
collection_name=COLLECTION_NAME,
anns_field="embeddings",
data=[[0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5]],
# highlight-next-line
filter=filter_slop1,
search_params={},
limit=10,
output_fields=["id", "text"]
)
print("Slop 1 result: ", result_slop1)
# Expected output:
# Slop 1 result: data: [[{'id': 461366973343948098, 'distance': 0.9949367046356201, 'entity': {'text': 'Deep learning machine algorithms require large datasets for training.', 'id': 461366973343948098}}, {'id': 461366973343948101, 'distance': 0.9710607528686523, 'entity': {'text': 'This article discusses various learning machine techniques and applications.', 'id': 461366973343948101}}]]
import io.milvus.v2.service.vector.request.SearchReq;
import io.milvus.v2.service.vector.response.SearchResp;
String filterSlop1 = "PHRASE_MATCH(text, 'learning machine', 1)";
List<Float> queryVector = Arrays.asList(0.1f, 0.2f, 0.3f, 0.4f, 0.5f);
SearchResp resultSlop1 = client.search(SearchReq.builder()
.collectionName(COLLECTION_NAME)
.annsField("embeddings")
.data(Collections.singletonList(queryVector))
.filter(filterSlop1)
.searchParams(Collections.emptyMap())
.topK(10)
.outputFields(Arrays.asList("id", "text"))
.build());
System.out.println("Slop 1 result: " + resultSlop1);
const filter_slop1 = "PHRASE_MATCH(text, 'learning machine', 1)";
const result_slop1 = await client.search({
collection_name: COLLECTION_NAME,
anns_field: "embeddings",
data: [0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5],
filter: filter_slop1,
limit: 10,
output_fields: ["id", "text"],
});
// go
# restful
export MILVUS_HOST="localhost:19530"
export COLLECTION_NAME="tech_articles"
export AUTH_TOKEN="your_token_here"
# Search数据
echo "Searching with PHRASE_MATCH filter (slop=1)..."
curl -X POST "http://${MILVUS_HOST}/v2/vectordb/entities/search" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer ${AUTH_TOKEN}" \
-d "{
\"collectionName\": \"${COLLECTION_NAME}\",
\"annsField\": \"embeddings\",
\"data\": [[0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5]],
\"filter\": \"PHRASE_MATCH(text, 'learning machine', 1)\",
\"searchParams\": {},
\"limit\": 10,
\"outputFields\": [\"id\", \"text\"]
}"
示例:slop = 2
此示例允许有 2 的容差,这意味着在 "machine" 和 "learning" 这两个词之间最多允许有两个额外的内容(或位置变换的词)。
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- Go
- cURL
# Example: Filter documents containing "machine learning" with slop=2
filter_slop2 = "PHRASE_MATCH(text, 'machine learning', 2)"
result_slop2 = client.search(
collection_name=COLLECTION_NAME,
anns_field="embeddings", # Vector field name
data=[[0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5]], # Query vector
# highlight-next-line
filter=filter_slop2, # Filter expression
search_params={},
limit=10, # Maximum results to return
output_fields=["id", "text"]
)
print("Slop 2 result: ", result_slop2)
# Expected output:
# Slop 2 result: data: [[{'id': 461366973343948097, 'distance': 0.9999999403953552, 'entity': {'text': 'Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence that focuses on algorithms.', 'id': 461366973343948097}}, {'id': 461366973343948098, 'distance': 0.9949367046356201, 'entity': {'text': 'Deep learning machine algorithms require large datasets for training.', 'id': 461366973343948098}}, {'id': 461366973343948099, 'distance': 0.9864400029182434, 'entity': {'text': 'The machine learning model showed excellent performance on the test set.', 'id': 461366973343948099}}, {'id': 461366973343948100, 'distance': 0.9782319068908691, 'entity': {'text': 'Natural language processing and machine learning go hand in hand.', 'id': 461366973343948100}}, {'id': 461366973343948101, 'distance': 0.9710607528686523, 'entity': {'text': 'This article discusses various learning machine techniques and applications.', 'id': 461366973343948101}}]]
// Example: Filter documents containing "machine learning" with slop=2
String filterSlop2 = "PHRASE_MATCH(text, 'machine learning', 2)";
SearchReq searchReqSlop2 = SearchReq.builder()
.collectionName(COLLECTION_NAME)
.annsField("embeddings") // Vector field name
.data(queryVector) // Query vector
// highlight-next-line
.filter(filterSlop2) // Filter expression
.searchParams(new HashMap<>())
.topK(10) // Maximum results to return
.outputFields(Arrays.asList("id", "text"))
.build();
SearchResp resultSlop2 = client.search(searchReqSlop2);
System.out.println("Slop 2 result: " + resultSlop2);
const filter_slop2 = "PHRASE_MATCH(text, 'learning machine', 2)";
const result_slop2 = await client.search({
collection_name: COLLECTION_NAME,
anns_field: "embeddings",
data: [0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5],
filter: filter_slop2,
limit: 10,
output_fields: ["id", "text"],
});
// go
#restful
curl -X POST "http://${MILVUS_HOST}/v2/vectordb/entities/search" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer ${AUTH_TOKEN}" \
-d "{
\"collectionName\": \"${COLLECTION_NAME}\",
\"annsField\": \"embeddings\",
\"data\": [[0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5]],
\"filter\": \"PHRASE_MATCH(text, 'machine learning', 2)\",
\"searchParams\": {},
\"limit\": 10,
\"outputFields\": [\"id\", \"text\"]
}"
示例:slop = 3
在这个例子中,slop 为 3 提供了更大的灵活性。过滤器搜索**"机器学习"**,允许单词之间最多有三个词元位置。
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- Go
- cURL
# Example: Filter documents containing "machine learning" with slop=3
filter_slop3 = "PHRASE_MATCH(text, 'machine learning', 3)"
result_slop3 = client.search(
collection_name=COLLECTION_NAME,
anns_field="embeddings", # Vector field name
data=[[0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5]], # Query vector
# highlight-next-line
filter=filter_slop3, # Filter expression
search_params={},
limit=10, # Maximum results to return
output_fields=["id", "text"]
)
print("Slop 3 result: ", result_slop3)
# Expected output:
# Slop 3 result: data: [[{'id': 461366973343948097, 'distance': 0.9999999403953552, 'entity': {'text': 'Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence that focuses on algorithms.', 'id': 461366973343948097}}, {'id': 461366973343948098, 'distance': 0.9949367046356201, 'entity': {'text': 'Deep learning machine algorithms require large datasets for training.', 'id': 461366973343948098}}, {'id': 461366973343948099, 'distance': 0.9864400029182434, 'entity': {'text': 'The machine learning model showed excellent performance on the test set.', 'id': 461366973343948099}}, {'id': 461366973343948100, 'distance': 0.9782319068908691, 'entity': {'text': 'Natural language processing and machine learning go hand in hand.', 'id': 461366973343948100}}, {'id': 461366973343948101, 'distance': 0.9710607528686523, 'entity': {'text': 'This article discusses various learning machine techniques and applications.', 'id': 461366973343948101}}]]
// Example: Filter documents containing "machine learning" with slop=3
String filterSlop3 = String.format("PHRASE_MATCH(text, '%s', %d)", "machine learning", 3);
SearchResp resultSlop3 = client.search(
SearchReq.builder()
.collectionName(COLLECTION_NAME)
.annsField("embeddings") // Vector field name
.data(queryVector) // Query vector
.filter(filterSlop3) // Filter expression
.searchParams(new HashMap<>())
.topK(10) // Maximum results to return
.outputFields(Arrays.asList("id", "text"))
.build()
);
System.out.printf("Slop 3 result: %s%n", resultSlop3);
const filter_slop3 = "PHRASE_MATCH(text, 'learning machine', 3)";
const result_slop3 = await client.search({
collection_name: COLLECTION_NAME,
anns_field: "embeddings",
data: [0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5],
filter: filter_slop3,
limit: 10,
output_fields: ["id", "text"],
});
// go
# restful
curl -X POST "http://${MILVUS_HOST}/v2/vectordb/entities/search" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer ${AUTH_TOKEN}" \
-d "{
\"collectionName\": \"${COLLECTION_NAME}\",
\"annsField\": \"embeddings\",
\"data\": [[0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5]],
\"filter\": \"PHRASE_MATCH(text, 'machine learning', 3)\",
\"searchParams\": {},
\"limit\": 10,
\"outputFields\": [\"id\", \"text\"]
}"
注意事项
-
为字段启用短语匹配会触发倒排索引的创建,这会消耗存储资源。在决定启用此功能时,请考虑对存储的影响,因为存储空间的占用会根据文本大小、唯一词元以及所使用的分析器而有所不同。
-
在 Schema 中定义 Analyzer 后,其设置将对该 Collection 永久生效。如果您认为不同的 Analyzer 更适合您的需求,可以考虑删除现有集合,并使用所需的 Analyzer 配置创建一个新 Collection。
-
短语匹配性能取决于文本的分词方式。在将 Analyzer 应用于整个 Collection 之前,请使用
run_analyzer方法查看分词输出。有关更多信息,请参阅Analyzer 概述。 -
过滤
filter中的转义规则:-
表达式中用双引号或单引号括起来的字符被解释为字符串常量。如果字符串常量包含转义字符,则转义字符必须用转义序列表示。例如,使用
\\来表示\,\\t来表示制表符\t,以及\\n来表示换行符。 -
如果字符串常量用单引号括起来,常量内的单引号应表示为
\\',而双引号可以表示为"或\\"。示例:'It\\'s milvus'。 -
如果一个字符串常量用双引号括起来,那么常量中的双引号应该表示为
\\",而单引号可以表示为'或\\'。示例:"He said \\"Hi\\""。
-