稀疏向量
稀疏向量(Sparse Vector)是信息检索和自然语言处理中的一种重要数据表示方法。虽然稠密向量(Dense Vector)因其出色的语义理解能力而广受欢迎,但在需要精确匹配关键词或短语的应用中,稀疏向量往往能够提供更为准确的结果。
概述
稀疏向量是一种高维向量的特殊表示方法,其大多数元素为零,只有少数维度上有非零值。如下图所示,稠密向量通常以连续数组的形式表示,每个位置都有一个值(如 [0.3, 0.8, 0.2, 0.3, 0.1])。相比之下,稀疏向量仅存储非零元素及其索引位置,通常表示为键值对列表(如 [{2: 0.2}, ..., {9997: 0.5}, {9999: 0.7}])。
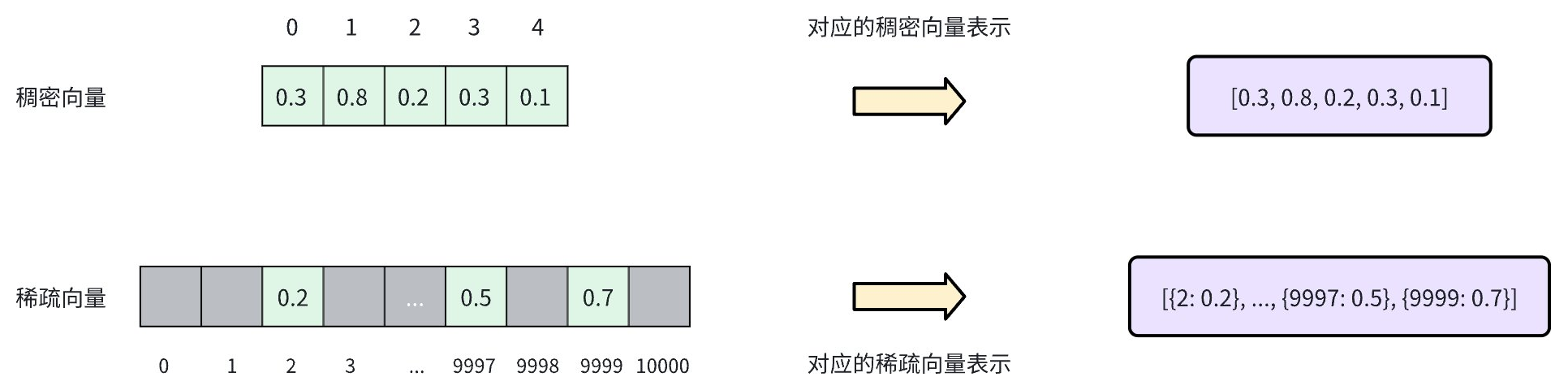
通过符号化和打分体系,文档由词袋向量表示,每个维度对应词表中的一个单词。文档中出现的单词在对应的向量中才有非 0 的取值。将所有非 0 的维度拼接起来就形成了该文档的稀疏向量表示。您可以使用如下两种方式生成稀疏向量:
-
传统统计方法:例如词频-逆文档频率(TF-IDF)和最佳匹配 25(BM25)等。这些方法基于词汇在语料库中的频率和重要性为词汇赋予权重,通过计算简单统计量作为每个维度的评分。每个维度代表一个词元。 Zilliz Cloud内置基于 BM25 算法的全文搜索功能,可自动将文本转换为稀疏向量,无需人工预处理。该方案特别适用于强调精确匹配和搜索精度的关键词检索场景。更多详情,请参阅Full Text Search。
-
神经稀疏向量嵌入模型:基于大量数据训练的可以生成使用稀疏向量表示的模型。通常都是 Transformer 架构的深度学习模型,能够根据语义上下文扩充和权衡待评估词句。Zilliz Cloud 也支持使用诸如 SPLADE 等外部的生成式稀疏向量模型。更多详情,请参阅 Embeddings。
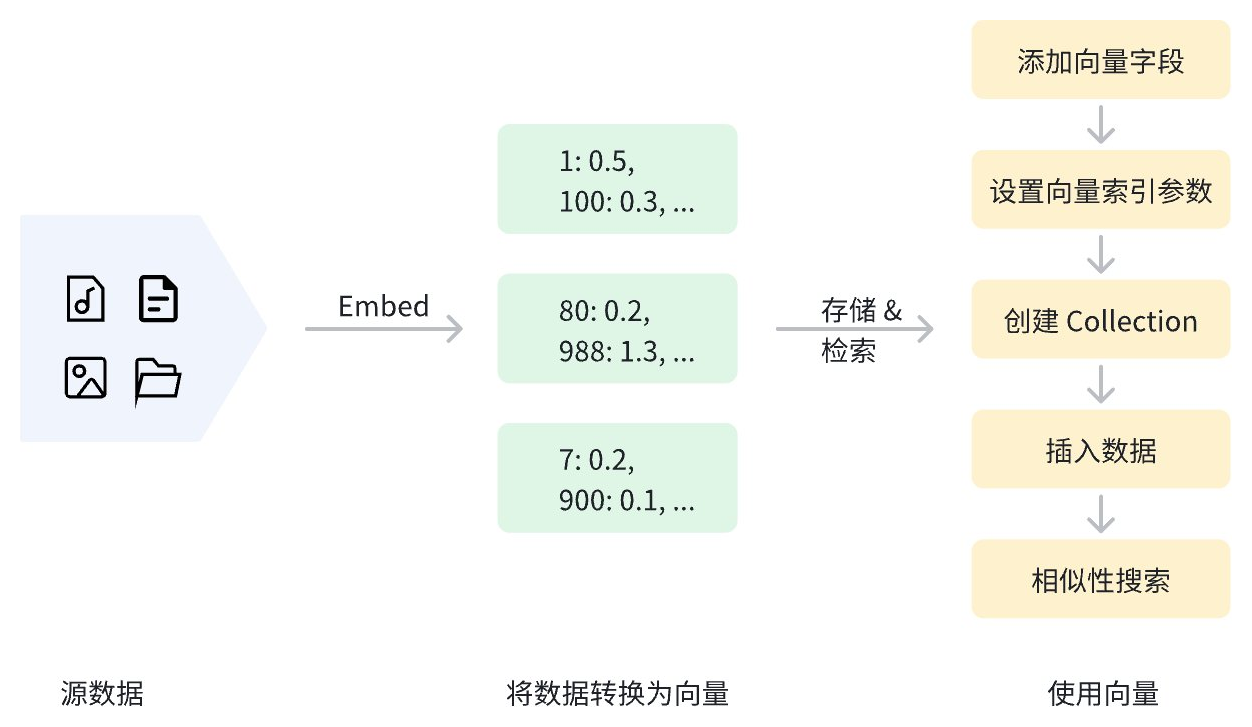
数据在向量化后,可以存储在 Zilliz Cloud 中进行管理和向量检索。下图展示了基本流程。
数据格式
Zilliz Cloud 支持用以下任意格式表示稀疏向量:
-
字典列表(格式为
{dimension_index: value, ...})# Represent each sparse vector using a dictionary
sparse_vectors = [{27: 0.5, 100: 0.3, 5369: 0.6} , {100: 0.1, 3: 0.8}] -
稀疏矩阵(使用 scipy.sparse 类)
from scipy.sparse import csr_matrix
# First vector: indices [27, 100, 5369] with values [0.5, 0.3, 0.6]
# Second vector: indices [3, 100] with values [0.8, 0.1]
indices = [[27, 100, 5369], [3, 100]]
values = [[0.5, 0.3, 0.6], [0.8, 0.1]]
sparse_vectors = [csr_matrix((vals, ([0]*len(idx), idx)), shape=(1, 5369+1)) for idx, vals in zip(indices, values)] -
元组迭代器列表(格式为
[(dimension_index, value)])# Represent each sparse vector using a list of iterables (e.g. tuples)
sparse_vector = [
[(27, 0.5), (100, 0.3), (5369, 0.6)],
[(100, 0.1), (3, 0.8)]
]
定义 Collection Schema
在创建 Collection 之前,需要定义 Collection Schema。这包括添加字段和定义将文本转换成对应稀疏向量表示的派生方法。
添加字段
要在 Zilliz Cloud 中使用稀疏向量,首先需要在创建 Collection 时定义用于存储稀疏向量的字段。这个过程包括:
-
设置
datatype为支持的稀疏向量数据类型,即SPARSE_FLOAT_VECTOR。该字段的值可以由您提供或由指定 VARCHAR 字段自动转换而来。 -
通常建议您将原始文本和向量字段都存入 Collection中。您可以使用 VARCHAR 字段来存放原始文本。
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- Go
- cURL
from pymilvus import MilvusClient, DataType
client = MilvusClient(uri="YOUR_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT")
schema = client.create_schema(
auto_id=True,
enable_dynamic_fields=True,
)
schema.add_field(field_name="pk", datatype=DataType.VARCHAR, is_primary=True, max_length=100)
schema.add_field(field_name="sparse_vector", datatype=DataType.SPARSE_FLOAT_VECTOR)
schema.add_field(field_name="text", datatype=DataType.VARCHAR, max_length=65535, enable_analyzer=True)
import io.milvus.v2.client.ConnectConfig;
import io.milvus.v2.client.MilvusClientV2;
import io.milvus.v2.common.DataType;
import io.milvus.v2.service.collection.request.AddFieldReq;
import io.milvus.v2.service.collection.request.CreateCollectionReq;
MilvusClientV2 client = new MilvusClientV2(ConnectConfig.builder()
.uri("YOUR_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT")
.build());
CreateCollectionReq.CollectionSchema schema = client.createSchema();
schema.setEnableDynamicField(true);
schema.addField(AddFieldReq.builder()
.fieldName("pk")
.dataType(DataType.VarChar)
.isPrimaryKey(true)
.autoID(true)
.maxLength(100)
.build());
schema.addField(AddFieldReq.builder()
.fieldName("sparse_vector")
.dataType(DataType.SparseFloatVector)
.build());
schema.addField(AddFieldReq.builder()
.fieldName("text")
.dataType(DataType.VarChar)
.maxLength(65535)
.enableAnalyzer(true)
.build());
import { DataType } from "@zilliz/milvus2-sdk-node";
const schema = [
{
name: "metadata",
data_type: DataType.JSON,
},
{
name: "pk",
data_type: DataType.Int64,
is_primary_key: true,
},
{
name: "sparse_vector",
data_type: DataType.SparseFloatVector,
},
{
name: "text",
data_type: "VarChar",
enable_analyzer: true,
enable_match: true,
max_length: 65535,
},
];
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"github.com/milvus-io/milvus/client/v2/column"
"github.com/milvus-io/milvus/client/v2/entity"
"github.com/milvus-io/milvus/client/v2/index"
"github.com/milvus-io/milvus/client/v2/milvusclient"
)
ctx, cancel := context.WithCancel(context.Background())
defer cancel()
milvusAddr := "localhost:19530"
client, err := milvusclient.New(ctx, &milvusclient.ClientConfig{
Address: milvusAddr,
})
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err.Error())
// handle error
}
defer client.Close(ctx)
schema := entity.NewSchema()
schema.WithField(entity.NewField().
WithName("pk").
WithDataType(entity.FieldTypeVarChar).
WithIsAutoID(true).
WithIsPrimaryKey(true).
WithMaxLength(100),
).WithField(entity.NewField().
WithName("sparse_vector").
WithDataType(entity.FieldTypeSparseVector),
).WithField(entity.NewField().
WithName("text").
WithDataType(entity.FieldTypeVarChar).
WithEnableAnalyzer(true).
WithMaxLength(65535),
)
export primaryField='{
"fieldName": "pk",
"dataType": "VarChar",
"isPrimary": true,
"elementTypeParams": {
"max_length": 100
}
}'
export vectorField='{
"fieldName": "sparse_vector",
"dataType": "SparseFloatVector"
}'
export textField='{
"fieldName": "text",
"dataType": "VarChar",
"elementTypeParams": {
"max_length": 65535,
"enable_analyzer": true
}
}'
export schema="{
\"autoID\": true,
\"fields\": [
$primaryField,
$vectorField,
$textField
]
}"
以上示例中,我们添加了三个名字段。它们分别为:
-
pk: 该字段用于存放 VARCHAR 类型的主键,其值为最大长度不超过 100 字节的自动生成的文本。 -
sparse_vector: 该字段用于存放 SPARSE_FLOAT_VECTOR 类型的向量字段,用于存储稀疏向量。 -
text: 该字段用于存放 VARCHAR 类型的文本字符串,最大长度为 1000 字节。
如果希望 or Zilliz Cloud 在插入数据时将指定的文本转换成稀疏向量。您还需要创建 Function。关于 Function 的更多内容,可以参考 Full Text Search。
为稀疏向量创建索引
为稀疏向量创建索引的过程和稠密向量类似,但指定的索引类型(index_type),距离度量类型(metric_type),和索引参数(params)有所差别。
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- Go
- cURL
index_params = client.prepare_index_params()
index_params.add_index(
field_name="sparse_vector",
index_name="sparse_auto_index",
index_type="AUTOINDEX",
metric_type="IP"
)
import io.milvus.v2.common.IndexParam;
import java.util.*;
List<IndexParam> indexes = new ArrayList<>();
indexes.add(IndexParam.builder()
.fieldName("sparse_vector")
.indexName("sparse_auto_index")
.indexType(IndexParam.IndexType.AUTOINDEX)
.metricType(IndexParam.MetricType.IP)
.build());
const indexParams = await client.createIndex({
field_name: 'sparse_vector',
metric_type: MetricType.IP,
index_name: 'sparse_auto_index',
index_type: IndexType.AUTOINDEX,
});
idx := index.NewSparseInvertedIndex(entity.IP, 0.2)
indexOption := milvusclient.NewCreateIndexOption("my_collection", "sparse_vector", idx)
export indexParams='[
{
"fieldName": "sparse_vector",
"metricType": "IP",
"indexName": "sparse_auto_index",
"indexType": "AUTOINDEX"
}
]'
上述示例使用索引类型为 SPARSE_INVERTED_INDEX,度量类型为 BM25。更多详细内容,可以参考如下内容:
创建 Collection
稀疏向量和索引定义完成后,我们便可以创建包含稀疏向量的 Collection。以下示例通过 create_collection 方法创建了一个名为 my_sparse_collection 的 Collection。
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- Go
- cURL
client.create_collection(
collection_name="my_collection",
schema=schema,
index_params=index_params
)
CreateCollectionReq requestCreate = CreateCollectionReq.builder()
.collectionName("my_collection")
.collectionSchema(schema)
.indexParams(indexes)
.build();
client.createCollection(requestCreate);
import { MilvusClient } from "@zilliz/milvus2-sdk-node";
await client.createCollection({
collection_name: 'my_collection',
schema: schema,
index_params: indexParams
});
err = client.CreateCollection(ctx,
milvusclient.NewCreateCollectionOption("my_collection", schema).
WithIndexOptions(indexOption))
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err.Error())
// handle error
}
curl --request POST \
--url "${CLUSTER_ENDPOINT}/v2/vectordb/collections/create" \
--header "Authorization: Bearer ${TOKEN}" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d "{
\"collectionName\": \"my_collection\",
\"schema\": $schema,
\"indexParams\": $indexParams
}"
插入稀疏向量
在插入数据时,您需要为所有在 Schema 中字义的字段提供相应的值,除了那些自动生成的字段(如因开启 AutoID 为自动生成的主键等)。如果您使用内置的 BM25 功能自动生成稀疏向量字段,在插入数据时,也不需要提供该字段的取值。
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- Go
- cURL
data = [
{
"text": "information retrieval is a field of study.",
"sparse_vector": {1: 0.5, 100: 0.3, 500: 0.8}
},
{
"text": "information retrieval focuses on finding relevant information in large datasets.",
"sparse_vector": {10: 0.1, 200: 0.7, 1000: 0.9}
}
]
client.insert(
collection_name="my_collection",
data=data
)
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import com.google.gson.JsonObject;
import io.milvus.v2.service.vector.request.InsertReq;
import io.milvus.v2.service.vector.response.InsertResp;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.SortedMap;
import java.util.TreeMap;
Gson gson = new Gson();
List<JsonObject> rows = new ArrayList<>();
{
JsonObject row = new JsonObject();
row.addProperty("text", "information retrieval is a field of study.");
SortedMap<Long, Float> sparse = new TreeMap<>();
sparse.put(1L, 0.5f);
sparse.put(100L, 0.3f);
sparse.put(500L, 0.8f);
row.add("sparse_vector", gson.toJsonTree(sparse));
rows.add(row);
}
{
JsonObject row = new JsonObject();
row.addProperty("text", "information retrieval focuses on finding relevant information in large datasets.");
SortedMap<Long, Float> sparse = new TreeMap<>();
sparse.put(10L, 0.1f);
sparse.put(200L, 0.7f);
sparse.put(1000L, 0.9f);
row.add("sparse_vector", gson.toJsonTree(sparse));
rows.add(row);
}
InsertResp insertResp = client.insert(InsertReq.builder()
.collectionName("my_collection")
.data(rows)
.build());
const data = [
{
text: 'information retrieval is a field of study.',
sparse_vector: {1: 0.5, 100: 0.3, 500: 0.8}
{
text: 'information retrieval focuses on finding relevant information in large datasets.',
sparse_vector: {10: 0.1, 200: 0.7, 1000: 0.9}
},
];
client.insert({
collection_name: "my_collection",
data: data
});
texts := []string{
"information retrieval is a field of study.",
"information retrieval focuses on finding relevant information in large datasets.",
}
textColumn := entity.NewColumnVarChar("text", texts)
// Prepare sparse vectors
sparseVectors := make([]entity.SparseEmbedding, 0, 2)
sparseVector1, _ := entity.NewSliceSparseEmbedding([]uint32{1, 100, 500}, []float32{0.5, 0.3, 0.8})
sparseVectors = append(sparseVectors, sparseVector1)
sparseVector2, _ := entity.NewSliceSparseEmbedding([]uint32{10, 200, 1000}, []float32{0.1, 0.7, 0.9})
sparseVectors = append(sparseVectors, sparseVector2)
sparseVectorColumn := entity.NewColumnSparseVectors("sparse_vector", sparseVectors)
_, err = client.Insert(ctx, milvusclient.NewColumnBasedInsertOption("my_collection").
WithColumns(
sparseVectorColumn,
textColumn
))
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err.Error())
// handle err
}
curl --request POST \
--url "${CLUSTER_ENDPOINT}/v2/vectordb/entities/insert" \
--header "Authorization: Bearer ${TOKEN}" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"data": [
{
"text": "information retrieval is a field of study.",
"sparse_vector": {"1": 0.5, "100": 0.3, "500": 0.8}
},
{
"text": "information retrieval focuses on finding relevant information in large datasets.",
"sparse_vector": {"10": 0.1, "200": 0.7, "1000": 0.9}
}
],
"collectionName": "my_collection"
}'
基于稀疏向量执行相似性搜索
要基于稀疏向量进行相似性搜索,您需要先准备查询向量和搜索参数。
- Python
- Java
- Go
- NodeJS
- cURL
# Prepare search parameters
search_params = {
"params": {"drop_ratio_search": 0.2}, # A tunable drop ratio parameter with a valid range between 0 and 1
}
# Query with sparse vector
query_data = [{1: 0.2, 50: 0.4, 1000: 0.7}]
import io.milvus.v2.service.vector.request.data.EmbeddedText;
import io.milvus.v2.service.vector.request.data.SparseFloatVec;
// Prepare search parameters
Map<String,Object> searchParams = new HashMap<>();
searchParams.put("drop_ratio_search", 0.2);
// Query with the sparse vector
SortedMap<Long, Float> sparse = new TreeMap<>();
sparse.put(1L, 0.2f);
sparse.put(50L, 0.4f);
sparse.put(1000L, 0.7f);
SparseFloatVec queryData = new SparseFloatVec(sparse);
// Prepare search parameters
annSearchParams := index.NewCustomAnnParam()
annSearchParams.WithExtraParam("drop_ratio_search", 0.2)
// Query with the sparse vector
queryData, _ := entity.NewSliceSparseEmbedding([]uint32{1, 50, 1000}, []float32{0.2, 0.4, 0.7})
// Prepare search parameters
const searchParams = {drop_ratio_search: 0.2}
// Query with the sparse vector
const queryData = [{1: 0.2, 50: 0.4, 1000: 0.7}]
# Prepare search parameters
export queryData='["What is information retrieval?"]'
# Query with the sparse vector
export queryData='[{1: 0.2, 50: 0.4, 1000: 0.7}]'
然后就可以使用 search 方法进行相似性搜索了。
- Python
- Java
- NodeJS
- Go
- cURL
res = client.search(
collection_name="my_collection",
data=query_data,
limit=3,
output_fields=["pk"],
search_params=search_params,
consistency_level="Strong"
)
print(res)
# Output
# data: ["[{'id': '453718927992172266', 'distance': 0.6299999952316284, 'entity': {'pk': '453718927992172266'}}, {'id': '453718927992172265', 'distance': 0.10000000149011612, 'entity': {'pk': '453718927992172265'}}]"]
import io.milvus.v2.service.vector.request.SearchReq;
import io.milvus.v2.service.vector.response.SearchResp;
SparseFloatVec queryVector = new SparseFloatVec(sparse);
SearchResp searchR = client.search(SearchReq.builder()
.collectionName("my_collection")
.data(Collections.singletonList(queryData))
.annsField("sparse_vector")
.searchParams(searchParams)
.consistencyLevel(ConsistencyLevel.STRONG)
.topK(3)
.outputFields(Collections.singletonList("pk"))
.build());
System.out.println(searchR.getSearchResults());
// Output
//
// [[SearchResp.SearchResult(entity={pk=457270974427187729}, score=0.63, id=457270974427187729), SearchResp.SearchResult(entity={pk=457270974427187728}, score=0.1, id=457270974427187728)]]
await client.search({
collection_name: 'my_collection',
data: queryData,
limit: 3,
output_fields: ['pk'],
params: searchParams,
consistency_level: "Strong"
});
resultSets, err := client.Search(ctx, milvusclient.NewSearchOption(
"my_collection",
3, // limit
[]entity.Vector{queryData},
).WithANNSField("sparse_vector").
WithOutputFields("pk").
WithAnnParam(annSearchParams))
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err.Error())
// handle err
}
for _, resultSet := range resultSets {
fmt.Println("IDs: ", resultSet.IDs.FieldData().GetScalars())
fmt.Println("Scores: ", resultSet.Scores)
fmt.Println("Pks: ", resultSet.GetColumn("pk").FieldData().GetScalars())
}
// Results:
// IDs: string_data:{data:"457270974427187705" data:"457270974427187704"}
// Scores: [0.63 0.1]
// Pks: string_data:{data:"457270974427187705" data:"457270974427187704"}
export params='{
"consistencyLevel": "Strong"
}'
curl --request POST \
--url "${CLUSTER_ENDPOINT}/v2/vectordb/entities/search" \
--header "Authorization: Bearer ${TOKEN}" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"collectionName": "my_collection",
"data": $queryData,
"annsField": "sparse_vector",
"limit": 3,
"searchParams": $searchParams,
"outputFields": ["pk"],
"params": $params
}'
## {"code":0,"cost":0,"data":[{"distance":0.63,"id":"453577185629572535","pk":"453577185629572535"},{"distance":0.1,"id":"453577185629572534","pk":"453577185629572534"}]}
有关更多搜索相关信息,请参考基本 ANN Search。